Data Catalog: What It Is & How It Drives Business Value
Share this article
A data catalog is no longer a mere inventory, glossary, or dictionary of your data. It’s an active data asset repository that acts as the context, control, and collaboration plane for your data estate. In this article, we’ll look at the components of data catalogs and how you can use them to drive business value in your organization.
Table of contents
What is a data catalog?
A data catalog acts as a single source of truth that enables data producers and data consumers to find, manage, and control access to data across your company’s data estate. It enables everyone - from data producers to business users - to create, publish, document, find, access, and report on data regardless of where it lives in the company.
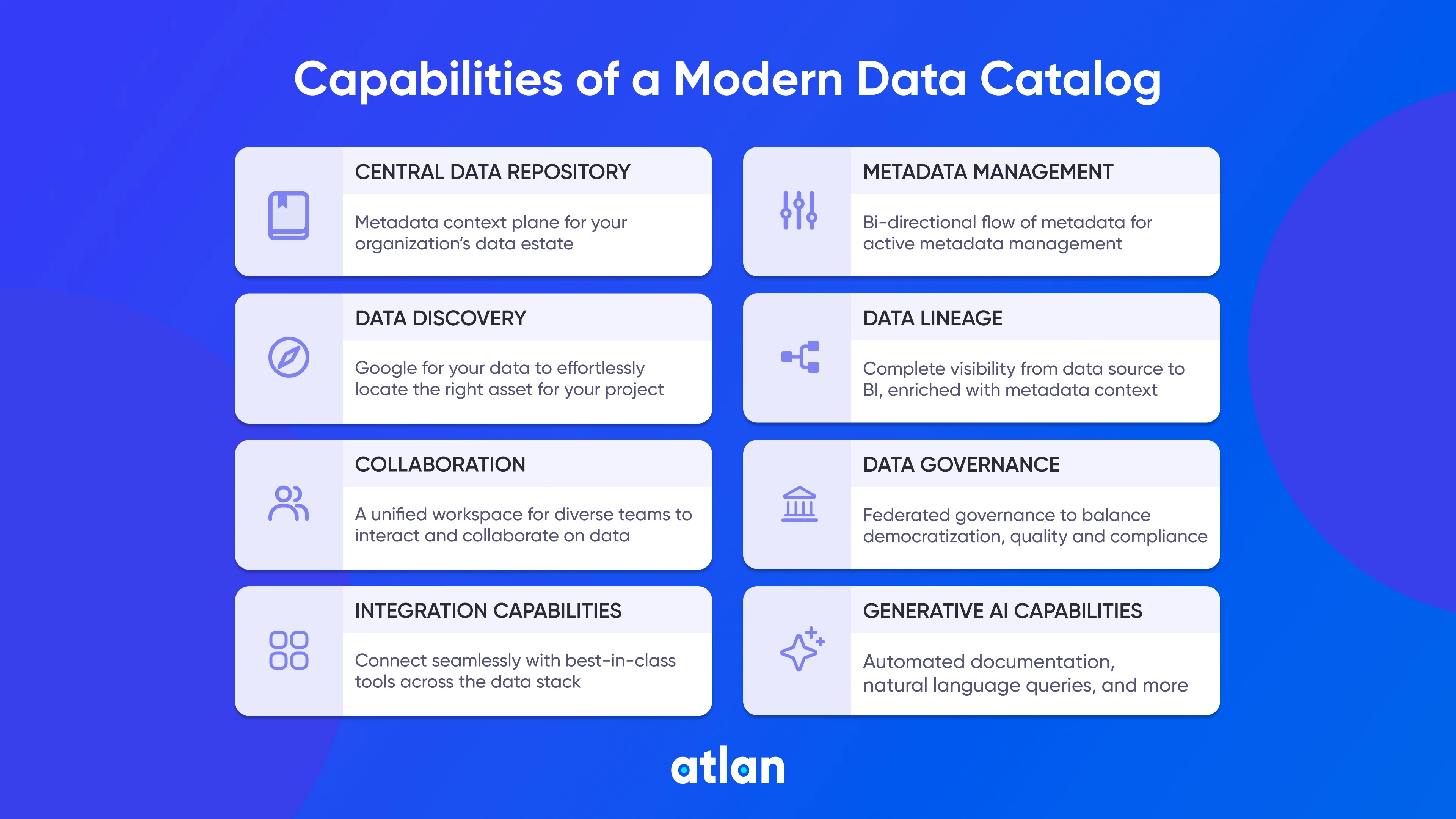
View data catalog capabilities visual representation in full size.
For example, let’s say you work as an analyst for a financial company. A data catalog could help you:
- Find relevant data. A data catalog could tell you which datasets you need to evaluate customer satisfaction with a new financial service.
- Trace, track, and trust data. If you wanted to know who edited a dataset, how old it was, or where it came from, a data catalog would tell you that.
- Collaborate. What if you need to work with someone in another department to understand and curate your dataset? That’s where collaboration features, such as shared workspaces, come in.
- Share your data. Make your findings available to other departments easily by publishing your data and associated metadata.
- Implement governance policies and access control. Enforce who has access to what data and document compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Business value and use cases for a data catalog
Back when they initially hit the scene, data catalogs were mainly about providing this central source of truth for your data. They’re still vital in fulfilling that function.
But the modern data catalog does so much more. Used correctly, a data catalog can improve data quality, reduce support costs, reduce compliance costs, and foster the creation of new, revenue-driving data products.
The key ways in which a data catalog drives business value are:
- Accelerating insights, data projects, and AI
- Creating trusted data for confident decision-making
- Safeguarding data security and compliance
- Realizing ROI on your data stack
Let’s look at these in detail, along with the use cases and data catalog capabilities that accompany them.
Accelerating insights, data projects, and AI
If you’re looking to buy a t-shirt online, you expect the most relevant results on top. You also know that something relevant for you may not be relevant for someone else — both your needs and experiences will be different.
This is 2024. Your teams expect the same ease of use when it comes to finding internal corporate data. Sadly, not many of them have it. A survey by Coveo found that almost 90% of business users had to search multiple locations to find the data they needed. That lack of discoverability can bring critical data projects grinding to a halt.
With a data catalog, you can establish a single, easy-to-use source of truth that enables everyone from data scientists to business analysts to find and understand the data they need to drive business value. This discoverability in turn drives the creation of new data projects, including machine learning and AI.
Use cases
Data discovery. An easy-to-use interface that enables searching for data across your entire data estate. A good data catalog uses capabilities such as search, filters, and recommendations to make finding the right data simple regardless of a user’s technical knowledge.
Data exploration. Sometimes, users need to dive deeper to find related data or mine existing data for insights. Data catalog capabilities such as natural language and no-code querying enable and encourage this deep exploration.
Root cause analysis. Data experts need the right tools to fix and pinpoint problems, such as erroneous reports or broken data pipelines. Data lineage capabilities enable data and analytics engineers to see all the upstream sources and downstream consumers of their data. That simplifies root cause analysis and reduces the time required to fix critical data issues.
Creating trusted data for confident decision-making
Even if users can find data in your company, they also need to know that they can trust it. Without clear documentation of where data comes from and what purpose it serves, users won’t feel confident they can rely on it for critical business decision-making.
Data without context is useless. Think of your new team member who’s trying to understand the field salesfigureNA_f. Or your team member in a different continent who’s been reading figures in the imperial system while all your calculations are in metric.
Data catalogs tackle this problem by gathering, keeping, and fostering the context around data (metadata). They also support capabilities for detecting and alerting on data quality issues and examining the impact of potential changes on downstream consumers.
Use cases
Metrics catalog. A data metrics catalog ensures that metrics across your organization are standardized, improving consistency and accuracy. It gets metrics out of their silos (and people’s heads) and makes them an official part of everyone’s daily vocabulary and workflows.
Metadata. Data catalogs capture, not just data, but the rich metadata that describes it and gives it context. They provide tools to capture and enrich metadata, including automated metadata capturing, certification workflows, and customizable metadata.
Impact analysis. What happens if you change the type or format of a data column in some data source? For most companies, the answer is “try it and find out” - which is a horrible way to learn.
Impact analysis leverages capabilities such as data lineage so that engineers and analysts can see exactly how downstream consumers, such as reports, may be affected by a data transformation change before you even commit it to source code.
Proactive data issue alerting. How do you know if your data is correct? With proactive alerting, you can detect and raise notifications automatically whenever the catalog detects anomalies.
Safeguarding data security and compliance
A correct and well-maintained inventory of data assets (a traditional catalog) may be a good starting point for governance. However, it can’t handle the velocity, volume, and complexity of data of today’s modern enterprises.
A data catalog that supports modern data governance uses automation, not only to collect and update data but to safeguard data at scale. It takes a shared responsibility approach to governance, fostering a culture of accountability among all stakeholders. It also uses automation to reduce errors and scale data governance operations.
Use cases
Data compliance management. A robust, modern data catalog should be able to gather data and metadata automatically from the complex variety of data sources used in your organization. That enables it to construct data lineage automatically, as well as drive propagation of data classification tags that secure sensitive information against unauthorized access.
A data catalog further enhances compliance management by enforcing governance policies at scale. For example, you can use a catalog to enforce masking on sensitive data. You can also set flexible security policies - e.g., enabling users to discover data by enforcing an access request workflow before granting full read permissions.
Realizing ROI on your data stack
Is your modern data stack costing you more than it’s making? As your data estate grows, so do inefficiencies that could be costing your company money. Data duplication, dark data, and out-of-date data are just some of the ways in which you could be losing value because you don’t have a 360-degree picture of your data.
Installing a data catalog gives an organization, often for the first time, a full, comprehensive view of its data estate. You can leverage this view to make key improvements to your data stack that significantly increase its business value and Return on Investment (ROI).
Use cases
Cost optimization. Using your data catalog, you can see which information is most used in your organization - as well as which data is going unused while also costing you money to store and process.
Data lifecycle management. Assign owners to data so that there are clear lines of responsibility for managing data across its lifetime. Use analytics to determine which data can be offloaded from data warehouses and stored in a much more cost-efficient manner (e.g., in warm or cold storage vs. hot access).
The next wave of data catalogs
The first generation of data catalogs provided a central location for finding data.
But today’s data catalogs do so much more. Organizations need better and faster ways to track data, assess the impact of changes, and help users share and collaborate on new data projects.
Modern data catalog tools take an active role in helping you manage and activate your data. They have the following distinctive features:
- Automation for faster time-to-value. Many first-gen data catalogs require an army of data stewards and other workers to keep them running. A modern data catalog utilizes no-code integrations to automate metadata ingestion and refresh. It also employs other innovative automation features, such as AI-powered suggestions for data enrichment and rules-based tagging of both upstream and downstream data.
- Lineage for a single pane of glass. Builds end-user trust by providing an end-to-end, automatically updated view of how your data travels through your data estate.
- Adoption by data and business teams. Gone are the days when a data catalog was a tool used exclusively by the IT team. A data catalog should support business users’ self-servicing data access and extracting value via BI reports as easily as it supports data engineers tracking down the root cause of data quality issues.
- Configurable and flexible for diverse teams and stacks. Supports configurable interfaces (e.g., metadata display) that show only what’s relevant for the current end-user and their job function.
- Extensible platform. Enables integrating deeply into your organization via open APIs, custom certification workflows, custom data connectors, and event-driven custom actions.
This is how we’re building Atlan.
- The latest Forrester report named Atlan a leader in Enterprise Data Catalog for DataOps, giving the highest possible score in 17 evaluation criteria including Product Vision, Market Approach, Innovation Roadmap, Performance, Connectivity, Interoperability, and Portability.
- Atlan enjoys deep integrations and partnerships with best-of-breed solutions across the modern data stack. Check out our partners.
Atlan already enjoys the love and confidence of some of the best data teams in the world including Nasdaq, Elastic, and HelloFresh — to name but a few. Check out what our customers have to say about us.
Share this article